
Flu Season: What You Need To Know
Are you prepared for the flu season? Arm yourself with facts about influenza from our infographic below and learn how to combat the flu this season.
Add This Infographic to Your Site

|
What you need to know about flu season:
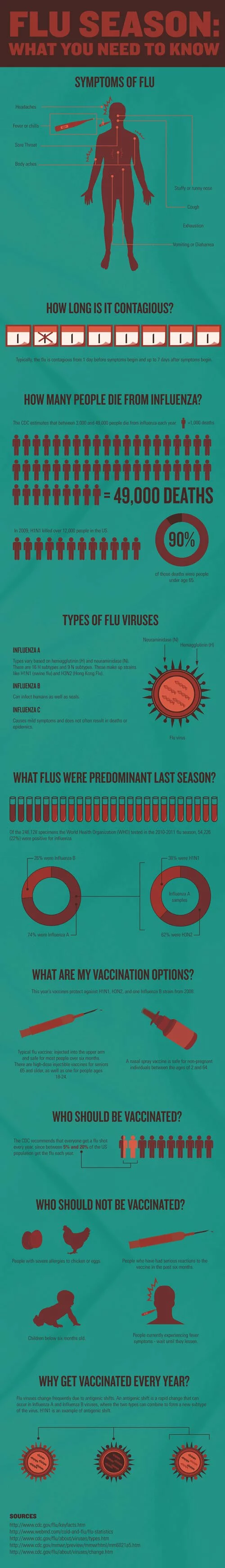
What are the symptoms of flu?
Headaches
Fever or chills
Sore throat
Body aches
Stuffy or runny nose
Cough
Exhaustion
Vomiting or diarrhea
How long is it contagious?
Typically, the flu is contagious from one day before symptoms begin and up to seven days after symptoms begin
How many people die from influenza?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that between 3,000 and 49,000 people die from influenza each year
In 2009, H1N1 killed more than 12,000 people in the U.S. About 90 percent of those who died were over the age of 65.
Types of flu viruses:
- Influenza A: Types vary based on hemagglutin (H) and neuraminidase (N). There are 16 H subtypes and 9 N subtypes. These make up strains like H1N1 (swine flu) and H3N2 (Hong Kong Flu)
- Influenza B: Can infect humans as well as seals
- Influenza C: Causes mild symptoms and does not often result in deaths or epidemics
What flus were predominant last season?
Of the 246,128 specimens the World Health Organization (WHO) tested during the 2010-2011 flu season, 54,226 (22 percent) were positive for influenza. About 26 percent were influenza B while the remaining 74 percent were Influenza A. Of the Influenza A samples, 38 percent were H1N1 while 62 percent were H3N2.
What are my vaccination options?
This years vaccines protect against H1N1, H3N2 and one Influenza B strain from 2008 A typical flu vaccine is injected into the upper arm and is safe for most people over six months old. There are high-dose injectable vaccines for seniors 65 and older, as well as one for people ages 18-24. A nasal spray vaccine is safe for non-pregnant individuals between the ages of two and 64.
Who should be vaccinated?
The CDC recommends that everyone get a flu shot every year, since between 5 percent and 20 percent of the U.S. population gets the flu each year
Who should not be vaccinated?
- Those with severe allergies to chicken or eggs
- People who have had serious reactions to the vaccine in the past six months
- Children under six months old
- People currently experiencing fever symptoms wait until they lessen
Why get vaccinated every year?
Flu viruses change frequently due to antigenic shifts. An antigenic shift is a rapid change that can occur in Influenza A and Influenza B viruses, where the two types can combine to form a new subtype of the virus. H1N1 is an example of an antigenic shift.
|


